Several technologies for reducing plastic waste have been developed with support from the Technology Development Programmes of Department of Science & Technology (DST).
 Novel technologies for converting Polystyrene Waste to fabric for Oil Spills Remediation
Novel technologies for converting Polystyrene Waste to fabric for Oil Spills Remediation
Scientists have developed an innovative way to convert polystyrene plastic waste like thermocol into a fabric that can absorb oil from water and hence will be effective in clearing up oil spills.
The technology by IIT-Hyderabad uses orange peels to recycle polystyrene plastic waste and involves a low-energy and cost effective scalable process.
The resultant fabric is hydrophobic but oleophilic. It is an illustration of novel, green technologies that can put both plastics and agro-waste to use. It can selectively absorb oil from oil-water mixture and hence can be used for oil-water separations leading to applications from day to day household cleaning in kitchen, restaurants, waste water treatment, to global requirement of oil spillage remediation in large water bodies.
To commercialize this technology, a start-up company, M/s. Restyro Technologies Pvt. Ltd. has also been incubated at IIT-H.
 New technology extends life of Reverse Osmosis Membranes
New technology extends life of Reverse Osmosis Membranes
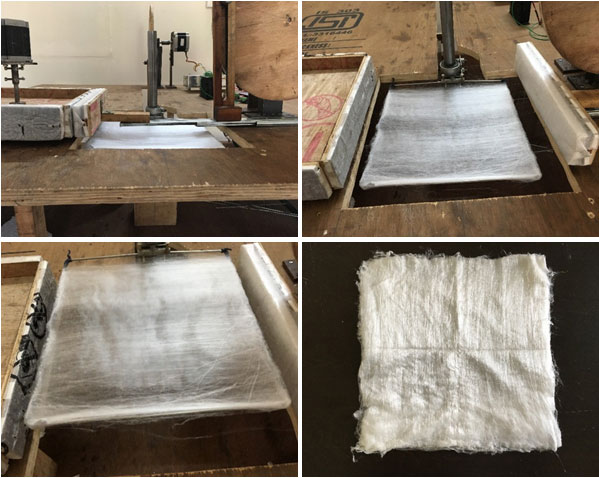
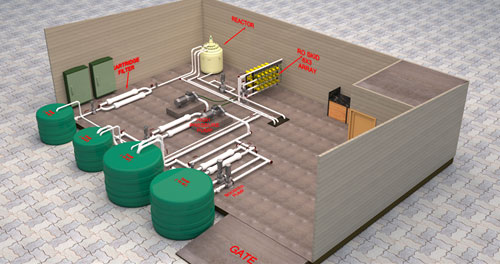
CSIR-Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute, Gujarat has found a technology for extending the life of membrane elements used for reverse osmosis like polymeric parts, adhesives and membrane sheets.
This will reduce the new membrane production and thus it will curb the green-house gas emission associated with production of these ingredients. Less membranes being discarded will require lower area of landfill disposal site and lower associated pollution. It will make the desalination environment friendly and more sustainable.
 Eco-friendly technology for recycling plastics of Waste Electrical & Electronic Equipment
Eco-friendly technology for recycling plastics of Waste Electrical & Electronic Equipment
Central Institute of Plastic Engineering and Technology (CIPET), Chennai has developed various value added formulations from the plastics waste generated from WEEE which contribute to 33 - 40% of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipments (WEEE).
The processing technologies involve a closed loop cycle without the emission of any toxic fumes. A technology demonstration plant (demo-e-waste recycling unit) is being set up by CIPET under this sponsored project which involves transfer of technology to interested entrepreneurs.