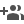Scientists have shown that the cold desert of Ladakh Himalaya once experienced large floods that rose much above the present-day river level. It implies that in the scenario of global warming, when the higher Himalaya regions are expected to respond dramatically, flood frequency in Ladakh may increase, which may call for serious urban and rural planning.
Large floods that naturally occur in major rivers of India fed by melting snow and glaciers and a continental scale precipitation regime of Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM) and Westerlies and East Asian Summer Monsoon (EASM) significantly modify the landscape and impact lives and economy of all that encroached into its geomorphic domain.
These floods are of various kinds and origin (Glacial/landslide lake outbursts, cloud bursts, excessively strong monsoon) and have different forcing factors and frequencies and therefore add large uncertainty in flood prediction models. An instrumental record of these floods is of ~100 years is not enough to understand the natural ramp of flood occurrences in the Himalayas, and therefore archive going deep into time is required.
A team of students and scientists lead by the Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology at Dehradun, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, travelled through the tough terrains of Zanskar and Indus drained Himalaya and looked minutely into geological signatures of past floods in Ladakh region that date between 15-3 thousand years before present. This study was recently published online in the Geological Society of America Bulletin.
Flood leaves a stack of fine sand and silts at places along its channel where the flood energy drastically reduces, for example, wider segments of river valleys, confluences, behind rock embayments which is called as Slack Water Deposits (SWDs). The SWDs were located at several locations along the Zanskar and Indus rivers, counted vertically for the number of floods, and were dated using technology called Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) and Accelerator Mass Spectrometry of 14C. The flood deposits were also analysed for their source.
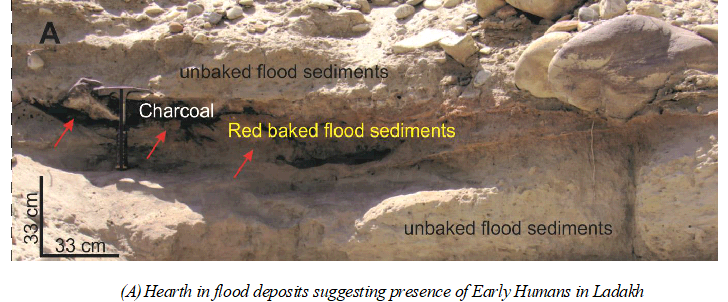
This analysis showed that the cold desert once experienced a large flood that rose to more than 30 m above the present-day river level. The active flood plains nearer to river were also utilized by Humans, possibly as camping sites and cooking as indicated by presence of hearths at several locations and levels of flood deposits.
Map Showing, the Geology of Ladakh, drained by the Zanskar and Indus Rivers and locations where paleoflood deposits (SWDs) are located.

The chronology of the flood deposits pointed towards three phases of increased flooding occurred in Ladakh after the period called Last Glacial Maximum (14–11, 10–8, and 7–4 (1000 years) or ka). These were times when due to warming, the Indian summer monsoon was active in Ladakh as well. The results also suggest that Ladakh floods are chronologically out-of-phase with those occurring in North-Eastern Himalayas and mainland China during the past 15 thousand years. This implies that the modern relationship between the ISM and EASM goes deep into more than 14 thousand years. Further, the rocks of Higher Himalayan Crystalline and Tethyan sequences equally act as hotspots of erosion in the regions during the flood phases.
The preliminary study of hearths suggested that there was an inbound migration of people along the mountain corridors of Ladakh after the Last Glacial Maximum when temperatures were relatively warmer, and hydrology of the region was supporting. According to the WIHG team, a detailed genomic and isotopic-based study of these anthropogenic relics may further help understand the geographical antiquity of migrating humans and the kind of food and vegetation they were living on.
Publication Link: doi: https://doi.org/10.1130/B35976.1