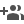An extremely bright, hydrogen deficient, fast-evolving supernovae that shines with the energy borrowed from an exotic type of neutron star with an ultra-powerful magnetic field has been spotted by Indian researchers. Deep study of such ancient spatial objects can help probe the mysteries of the early universe.
Such type of supernovae called SuperLuminous Supernova (SLSNe) is very rare. This is because they are generally originated from very massive stars (minimum mass limit is more than 25 times to that of the Sun), and the number distribution of such massive stars in our galaxy or in nearby galaxies is sparse. Among them, SLSNe-I has been counted to about 150 entities spectroscopically confirmed so far. These ancient objects are among the least understood SNe because their underlying sources are unclear, and their extremely high peak luminosity is unexplained using the conventional SN power-source model involving Ni56 - Co56 - Fe56 decay.
SN 2020ank, which was first discovered by the Zwicky Transient Facility on 2020 January 19, was studied by scientists from Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) Nainital, an autonomous research institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) Govt. of India from February 2020 and then through the lockdown phase of March and April. The apparent look of the SN was very similar to other objects in the field. However, once the brightness was estimated, it turned out as a very blue object reflecting its brighter character.
The team observed it using special arrangements at India’s recently commissioned Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT-3.6m) along with two other Indian telescopes: Sampurnanand Telescope-1.04m and Himalayan Chandra Telescope-2.0m. They found that the outer layers of the onion structured Supernovae had been peeled off, and the core was shining with a borrowed energy source. The study led by Amit Kumar, a Ph.D. student working under Dr. S. B. Pandey published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, suggested a possibly powering source from an exotic type of neutron star with an ultra-powerful magnetic field (magnetar) with a total ejected mass of ~ 3.6 一 7.2 times the mass of the sun.
The study established the role of 3.6. DOT in exploring very rare distant SLSNe in the future. Deeper investigations could explore the underlying physical mechanisms, possible progenitors, and environments hosting such rare explosions and their possible associations with other energetic explosions like Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) and Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs).
Fig.1: Finding chart of SN 2020ank (∼5×4 arcmin2 field) along with other local standard stars (marked in circles, IDs 1–7). The R-band image (exposure time = 5 min) observed on 2020 March 19 using the 4K×4K CCD Imager mounted at the axial port of the 3.6m DOT facility. The location of SN is marked with a blue crosshair. North and East directions are also indicated in the image (taken from Kumar Amit et al. (, 2021, MNRAS, 502, 1678K).
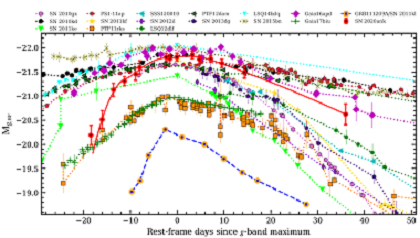
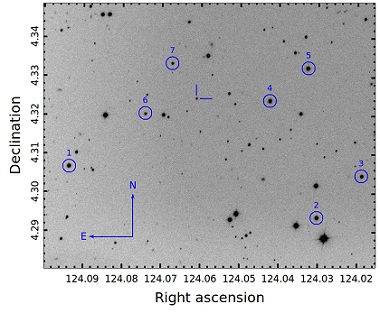
Fig.2: Comparison of the rest-frame g-band light curve of SN 2020ank (in red) with other well-studied SLSNe-I (taken from Kumar Amit et al. (2021, MNRAS, 502, 1678K).
Publication details: https://academic.oup.com/mnras/article/502/2/1678/6103929
Amit Kumar et al., 2021, MNRAS, 502, 678
For more details, Amit Kumar and Dr. S. B. Pandey, 09557470888, shashi[at]aries[dot]res[dot]in can be