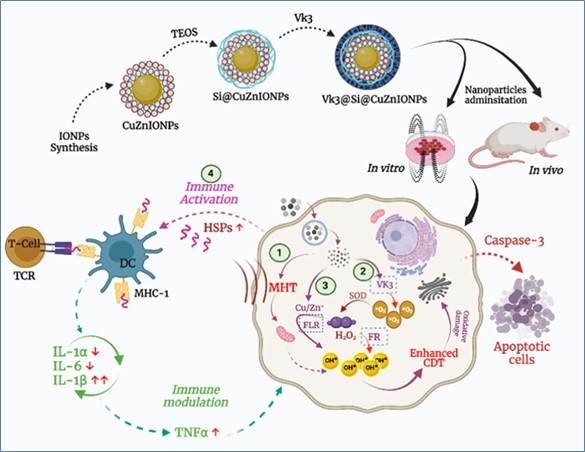
A new efficient system of cancer treatment using vitamin k3 (Vk3)-loaded copper zinc ferrite nanoparticles having therapeutic capabilities, could benefit millions of cancer patients worldwide.
With the ever-increasing prevalence of cancer cases worldwide, newer approaches to cancer therapy are increasingly needed to tackle the problem. Since conventional cancer therapies such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery have significant drawbacks such as resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs, adverse effects and lower efficacy, development of nanotherapies that can target hypoxic (when oxygen is not available in sufficient amounts at the tissue level) tumors, with minimum side-effects is necessary.
At present, magnetic hyperthermia-based cancer therapy (MHCT) therapy has been shown to be therapeutic. However, in most cases, it is not as effective due to the generation of lower levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a hypoxic tumor microenvironment (TME) and low heat transmission.
Dr. Deepika Sharma and her team at Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute of Department of Science and Technology used vitamin k3 (Vk3)-loaded copper zinc ferrite—magneto thermodynamic (MTD) treatment (that integrates magnetic hyperthermia and chemodynamic therapy by amalgamating the effects of ROS generated by magneto thermodynamics and the immunological impact of heat) to overcome this shortcoming by causing irreversible oxidative damage to the tumor cells leading to complete tumor eradication within 30 days of treatment.
Vk3@Si@CuZnIONPs is capable of amplifying ROS concentrations selectively in cancer cells, thus leading to cancer-specific and selective killing of cancer cells without affecting normal cells. The rationale behind this is that Vk3 is believed to have a high redox cycling efficiency in cancer cells. Furthermore, the hyperthermia conversion performance of nanoparticles could effectively produce endogenous heat under AMF, which makes DNA more sensitive to ROS damage.
Dr. Anjali Chauhan a research associate of Dr. Sharma’s laboratory has successfully engineered Vk3@Si@CuZnIONPs. Vk3@Si@CuZnIONPs. These nanoparticles are capable of amplifying ROS concentrations selectively in cancer cells, thus leading to cancer-specific and selective killing of cancer cells without affecting normal cells. The rationale behind this is that Vk3 is believed to have a high redox cycling efficiency in cancer cells. Furthermore, the hyperthermia conversion performance of nanoparticles could effectively produce endogenous heat under AMF, which makes DNA more sensitive to ROS damage.
“Vk3@Si@CuZnIONP-mediated MTD promotes rapid tumor growth via the HSPs, activates the dendritic cells, in turn, triggering the immune response through the secretion of cytokines. This has led to a highly complex collaborative system to overcome tumors through the coupled response of high ROS and heating based immunological effects,” said the scientists associated with the study.
The combined MTD-related ROS and heat-related immunological effect resulted in a synergistic anticancer response. The researchers achieved tumor inhibition rate of 69% within 20 days of MTD treatment, and complete tumor eradication within 30 days.
The research which was published in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces is may lead to an adjuvant or alternative cancer therapy in the future.
Link to paper: 10.1021/acsami.3c01702.