List of Focal Points of State S&T Councils![]() 26.17 KB
26.17 KB
"However large may be the central Government's investment of energy and resources in the scientific and technological effort, it must take the states along if developmental goals are to be attained."
The state level machinery (State S&T councils) has to take the role of a major 'Prime Mover' while the centre could play a very catalytic and effective role in encouraging the initiative of state Governments.."
Bharat Ratna Late Shri C. Subramaniam Assistance for Development of State Councils for Science & Technology
Assistance for Development of State Councils for Science & Technology
Compendium of the Annual Conclave of State S&T Councils
![]() 15.85 MB
15.85 MB
Background
The initiative to establish State Councils for Science & Technology was first taken in 1971 when the then Minister for S&T and Chairman, National Committee for Science & Technology (NCST), Shri C Subramanam wrote to Chief Ministers of all the States stressing that irrespective of large investments of the Central Government in S&T in various sectors and institutional infrastructure, the Central S&T Agencies must take the States along if the development goals are to be attained. By the end of Fifth Five Year Plan, Karnataka, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal were the four States, who had established their State S&T Councils. While these few States responded to the idea of State S&T planning & promotion, it became clear that a sustained effort was needed to establish and develop the State Councils for Science & Technology.
As a result, the process of impetus for State level planning and Promotion of Science & Technology began in the Sixth Five Year Plan (1980-85) and continued through the subsequent Five Year Plans, primarily through this plan programme, formerly known as, "Assistance for development of State Councils for Science and Technology".
State Science & Technology Councils have been set-up in all the States and Union Territories. Several States have also formed a separate Department of Science & Technology. The State Councils are normally chaired by Chief Ministers of respective States or by an eminent scientist.
Evolving Roles of DST
Department of Science & Technology (DST), Government of India (GOI), played a catalytic role by facilitating the State Governments in establishing and developing the State S& T Councils on S&T and by providing support for their technical secretariats. Concurrently DST (GOI), in collaboration with respective State Councils, organized all India thematic meetings/workshops whose recommendations helped identify activity-areas for promotion by the State S&T Councils. DST also organised periodic review meetings to discuss the status of various S&T programmes and to plan the strategy for future. Regional Meetings organised by DST facilitated review of state S&T structures and identification of areas of mutual cooperation between States.
On completion of 10 years of this programme, a Decennial Review was held to assess the strengths and weaknesses of this programme vis-à-vis DST's performance. This review indicated desire for a phase change geared towards programmatic support and strengthening linkages between State S&T Councils and Central S&T Agencies by suitably dovetailing various programmes of State S&T Councils with those of Central S&T Agencies.
It was also realised that these State S&T Councils, since their formation have now come of age to initiate a phase where resources in terms of expertise and technology promoted and generated by the Central and State S&T Agencies be pooled together to undertake joint S&T programmes.
Encouraging Initiatives
DST's support has facilitated State S&T Councils to embark upon novel initiatives resulting in a number of success stories. The illustrations below are testimony to catalytic but effective role played in encouraging the initiative of State S&T Councils.
Student Project Programme (Karnataka):
a highly successful and probably longest continuing programme aimed at encouraging students to use their talent for solving local problems and improving quality of higher education in engineering and sciences, streams.

Exhibits displayed during Student Project Programme Seminar cum Exhibition
Cleaner and Fuel Efficient Technologies (Punjab):
successful development and introduction of Air pollution control equipment for cupola furnaces, rice shellers and induction furnaces which not only reduced pollution but also improved fuel efficiency.

Field visit to Rice Sheller
Solar Passive Housing Technology (Himachal pradesh):
a technology for effectively utilising solar energy for day lighting and space heating purposes, successfully introduced and widely replicated through promotional as well as policy instruments.

Himurja Bhawan - A building designed on Solar passive concepts
Defluoridation of Drinking Water (Rajasthan):
successful development and demonstration of handpump attached defluoridation unit, widely acclaimed for its user-friendly features and readily accepted by Public Health Engineering Department.

>Handpump attached defluoridation unit
Development of Technology for degumming of Ramie Fibre (Assam):
an initiative that has resulted in generating income opportunities as rural ramie grower can now produce value added finished products.

Degumming of Ramie Fibre
Promoting Catalytic Linkages
State Science & Technology Programme has been playing a catalytic role to promote other State Oriented S&T activities of DST as well as other Central S&T Agencies. This has been done through, provision of manpower dedicated for the programme, providing forum for interaction between State S&T Councils and these programmes and organising thematic meetings to ensure focussed attention.
Science Communication: creation of scientific temper through children science Congress, Science behind miracles, National Science day etc. activities facilitated.

National Science Day Celebration
Natural Resources Data Management system (NRDMS):
increase in the efficiency of use of natural resources of district through application of scientific management principles and its replicability throughout the state. NRDMS District Centres and programmes being implemented in various states.
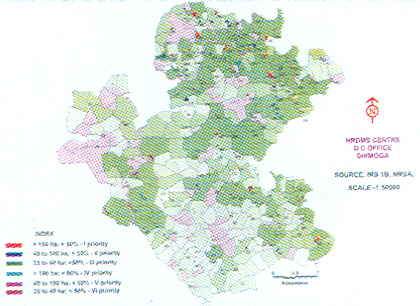
Prioritisation of Minor Irrigation Tanks for Rejuvenation based on Ayacut Area in Sorab Taluk, Shimoga District, Kamataka
Patent Awareness:
Patent awareness workshops in various states and Patent Facilitating Centres -(PFCs) in various State S&T Councils.

Patent awareness workshop at Bihar Council on S&T
Societal S&T Programmes:
replication of technology models for-rural application as well as development of location specific need based technologies.

Prototype "Pedal Operated Rice Mill"
S&T Human Resource Development:
organisation of national level meets, workshops, symposium, young scientists fellowships, etc for the benefit of scientific community in State S&T institutions.

Entrepreneurship Development Programmes:
to provide self-employment for S&T manpower and promoting S&T Entrepreneurship programmes in the States.

Leg Operated wool spinning charkha (Medulary Charkha)
Programmatic Support
The beginning of Programme Support under the scheme in the Ninth Plan addressed itself to need felt during Eighth Plan to accelerate S&T activities at the State level so as to ensure integration of S&T for overall socio-economic development with special emphasis on Location Specific Research & Technology Development, Adaptation and Transfer, S&T studies/surveys and information exchange & experience sharing on specific S&T programmes. This impelled a pro-active approach by DST to have synergy of efforts.
Pilot Scale Demonstration Projects:
support for setting up Pilot scale demonstration projects including field trials etc based on technologies developed by Central S&T Agencies/ Labs/ Institutions etc. relevant to the State needs.

Penstock laying work of Micro Hydel Project at Nagaland in Progress
S&T studies & surveys: support for carrying out S&T studies / surveys including techno-economic analysis, simulation modeling and studies etc. and development of State S&T database, S&T resources, State S&T policy issues, specific status reports etc. leading to specific action plan for project generation.

Traditional Milling Process, Namda Craft
Location specific research & technology development:
support for identifying/projectising S&T programmes and for development oriented location specific research and technology development.

Location Specific Research of Root Rot disease of Castor
Replication of success models: support for replication of projects/ programmes in other interested States based on successful experiences of a State S&T Council/State S&T Institute/ NGOs etc. Package for Sustainable Transformation of Rural Areas (SuTRA) developed by Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, proposed for replication at Rajasthan, AP and MP.
Information Exchange & Experience Sharing: support for meetings/ workshops and other means of information exchange and interaction of S&T experts and / or of S&T field activists etc, Workshops on dissemination of specific technology, Project/ programme formulation workshops.

A Scene of Specialised Training on Glazed Terracota
Awareness & Training: awareness and training on specific innovative technologies/ packages developed /propagated by State S&T department/ Council requiring special S&T inputs and also on specific S&T topics/themes and management of State S&T programmes.

Training on Mushroom Cultivation at Mushroom Spawn Centre
Salient Achivements
Reverse Osmosis Desalination Plant - Rajasthan & Gujarat:
converts brackish/hard water to potable drinking water.

Treatment of Important Poultry Diseases, Namakkal - Tamil Nadu:
monitoring, surveillance and prompt control of widely prevalent diseases of poultry.

Poultry Farm at Namakkal
Plasma Pyrolysis Plant - A&N , Goa, H.P., Sikkim: plasma assisted thermal. disintegration of plastic bags to overcome the plastic menace facilitating environment friendly disposal, can also treat hospital waste.

Plasma Pyrolysis unit at Goa
Installation of Hydrams - H.P :
an appropriate cost effective and practical technology to harness irrigation potential of streams in hilly regions, integrated with ferrocement technology and community irrigation concepts for optimised performance.

A Hydraulic Ram Pump (HRP) at Work
Cupola furnace modifications - Bihar & Haryana:
a suitable cost effective technology for controlling air pollution developed by Punjab State Council for Science & Technology.

Cupola installed at Kaithal, Haryana
Cardamom drier - Sikkim:
a fuel efficient technology with minimum wastage, higher yield and better quality.

Cardamon Drier, Sikkim
Inventory of Medicinal Plants - Andaman & Nicobar Islands:
a scientific documentation of medicinal & aromatic wealth of Islands.

Research Team of N.B.R.I & Forest Officers in Shompen Hut, Campbell Bay
Future Thrust
While continuing the catalytic role in encouraging the State Government's initiatives, the department would launch certain programmes of importance identified through various consultations pro-actively. The department would strive to evolve and support certain joint programmes focusing on multi-sectoral area based approach to rural / regional development in co-operation with multiple State & Central Institutions, NGO's and State S&T Councils. These areas would be so identified where S&T intervention could significantly improve the existing socio-economic conditions. Demonstration and Field trials of socially relevant technologies would specially be encouraged. Interaction between State S&T Councils in similar ecological zone has been initiated and would be promoted further in future to facilitate joint S&T Programme formulation.
DST would welcome proposals having clearly established linkages of S&T to overall development of the state. The area identified should have potential to contribute in socio-economic upliftment of the people of state. DST encourages formulations of proposals through consultative process and interested organisations are welcome to discuss ideas, concepts, proposed activities etc. relevant to state needs.
Format for Core Support Grant under SSTP![]() 622.5 KB
622.5 KB
Guidelines and Format for Submittion of Project Proposals![]() 192.95 KB
192.95 KB
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 | 2017-2018 | 2018-19 | 2019-2020 | 2020-21 |
Compendium
| 2020 | 2019 |
For more information Contact :
Dr. Debapriya Dutta
Head & Scientist "G" / Adviser
Societal Mission & Science for Equity Empowerment and Development (SEED) Divisions - State S&T Programme (SSTP)
Department of Science & Technology, Government of India
Tel. 011-26964793 / 26590558
E-mail : ddutta[at]nic[dot]in
Dr. Rashmi Sharma
Scientist F
Societal Mission & Science for Equity Empowerment and Development (SEED) Divisions - State S&T Programme (SSTP)
Department of Science & Technology
Technology Bhawan
New Mehrauli Road
New Delhi-110 016.
Email:r[dot]sharma72[at]nic[dot]in
Ph:011-26590541